Impact of Google Changes on Long Tail Search and Website R.O.I.
Search results page have changed dramatically since 2007, and this past year 2011 saw many big changes continue. 2012 is off to a ridiculously fast start of algorithm changes and enhancements. If you struggle to keep on top of the many changes in play, or if you chase the SEO tactic of the month, you will be in trouble in no time.
In May 2007, Google launched universal search, which added new searchable content such as news results, images, videos, local business listings with maps and a variety of other content types beyond the traditional 10 blue links on a page. In 2010, Google added Instant Search, a feature that changed the search results page while users typed in the search box.
Both of those, along with countless other feature enhancements, have changed the way in which Internet users interact with search results.
These three major changes really change the landscape for search marketing strategies;
- Google Instant
- Google Panda
- Google Encrypted
Change number #1 – Google instant
What is Google instant? Google Instant is a new search enhancement added in September of 2010 that displays search results while you type. The intent of Google instant is to display better search results, faster. The impact of Google Instant means that a user can scan search results page while still typing in their keyword query.
Example:
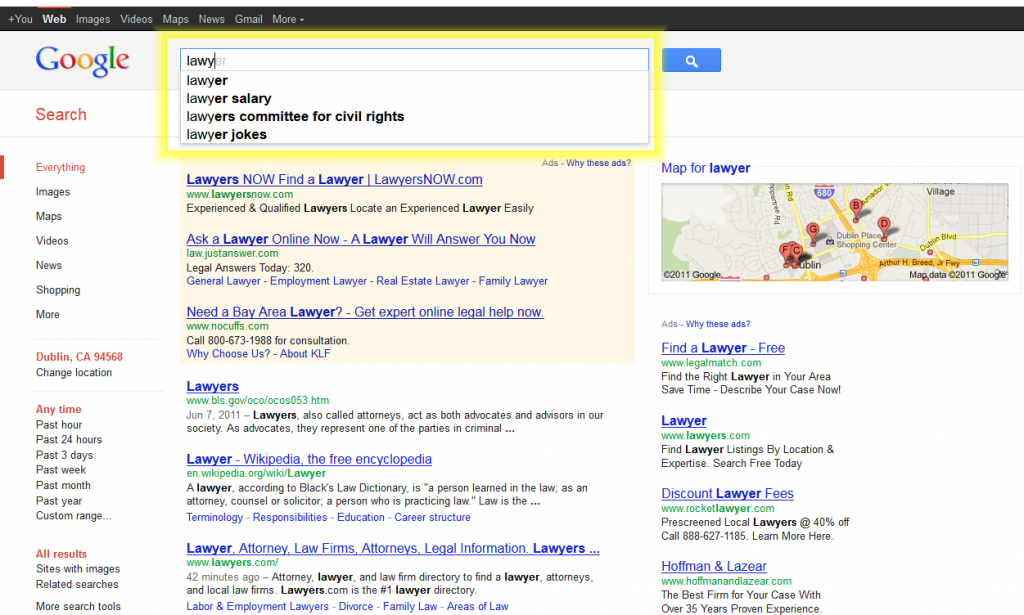
The primary visual difference is that users dive right into content much faster than before basically because a full search phrase is not required to display results. While this improvement has been pitched as a user benefit, remember that Google is a business and they see an enormous benefit to their data centers processing time.
What does Google Instant mean for long tail search?
Simply stated, it means that search engine optimization methodology must change to accommodate Instant results. Usually, internet users tend to skim Meta descriptions to verify the relevancy of the search results to their intended search query. A common SEO tactic was to place strong calls to action in the Meta description to grab searchers’ attention and stand out from the other results and get the user to click on the website. With the advent of Google Instant, more emphasis is now placed on the Title Tag because it is something the users can review quickly for relevance to their intended search. However, with results changing so quickly, we see calls to action potentially moving into the Title tag as users spend less time examining the results and will rely more on those parts of the result they can examine quickly.
Root keywords in the Title Tags
Since Google Instant presents results before the search user even finishes typing them in, root keywords of long tail terms becomes more even more important.
Take for example a keyword like lawyer and its derivates where the root is the first word of the phrase (ex. lawyer for business, lawyer in Los Angeles). Using Google Instant, the organic results for the keyword “lawyer” will be displayed when users start typing any derivative. What’s the impact? The exact match volume for “lawyer” is 353,000,000. Google Instant increases that exact match volume to (353,000,000 + Exact volumes of all keywords that start with the word “lawyer”).
Long tail traffic:
Long tail keywords that contain a root word at or towards the beginning of the phrase will see a decline in traffic. If you optimized your site for “lawyers” this is a positive for your SEO program. If you optimized your site for long tail legal terms on the other hand, this would hurt your strategy significantly.
Click through rates:
All results including top paid positions and organic listings are pushed further down the page with the inclusion of Local. Instead of 4-5 listings being displayed above the fold you’re looking at 1-2, depending on your resolution. This change in CTR will impact how much effort SEOs are willing to put towards ranking for a particular keyword. Just like with paid search where you weight the CPC of the position against the business impact, SEOs have to weight how much additional effort it would take to increase a keyword one position versus the business impact.
Change #2 – Google Panda
What is Google Panda aka “Farmer”?
Panda refers to the 2011 changes to the search algorithm used by Google to improve search engine results pages (SERP’s). This change was made to reduce the rank of “low quality sites” in the search results and return higher content quality sites to Google’s users. While most SEO’s believe that Panda is a content quality element within the search algorithm, it also appears to score link quality as well.
How Panda Works
Google Panda was constructed using an algorithm update that includes artificial intelligence in a more advanced and scalable method than was previously possible. Google’s machine learning algorithm searches for similarities between Users found websites of high quality and low quality. Numerous fresh ranking factors are brought into the Google algorithm, severely diminishing the value and importance of older ranking factors such as PageRank.
Content quality becomes even more important in a post-Panda world. The meaning of quality content changes quite a lot. Content written strictly for SEO purposes with correct spelling, good grammar, and appropriate keyword density is the cost of entry but this content does not really make a dent in the Panda metrics that indicates great unique on page content. The bar is raised to content that makes everyone who reads it say “Wow, I want to engage with this and to share it with others”. High quality content triggers user engagement signals onsite and via web 2.0 properties like Facebook or Twitter. These user metrics are totally different social signals to optimize, instead of optimizing simply for keywords.
Key user metrics and relevant engagement signals.
Comparing how a website functions relative to other sites in the same niche produces a different set of important metrics for post Panda performance. These newer key metrics include;
- Click Through Rate. If your CTR in the search results is low, the site is likely to suffer in traffic and rankings. Is the domain name relevant to the search query? Does it inspire user confidence or does it appear “spammy” with multiple hyphens and stuffed keywords?
- Bounce Rate. Are they bouncing or are the browsing?
- Time On Site. Do users visit and spend some time on your site, or do they go away immediately?
- Browse Rate. If users are reading more than one page, the content might actually be engaging, but if no one clicks on a second page the site is in serious trouble.
- Linking Root Domain Diversity. Are you getting visitor traffic from a number of different sources and distinct areas locally, regionally or nationally? Link diversity and quality of the links is more important than simple link quantity.
All of these data point as well as others are captured in the Panda intelligent learning machine protocol and the results are added into the algorithm for updating. This helps to explain the frequency of the Panda updates and is why you do not see daily or weekly updates.
What does Panda Mean for content?
Change #3 – Google Encrypted
What is Google Encrypted or “SSL Search”?
Google Search Encryption is a procedure that facilitates secure connections for Internet services such as web browsing, e-mail, instant messaging, and other online data exchanges. When a user logs into their Google account before doing online queries, their searches are completed via SSL. That logged-in users search queries and search traffic are then encrypted so third parties that might have easy access to that information can no longer easily see the encrypted queries.
They way this process works under most circumstances is, a logged in user now sees https://www.google.com when performing search queries. These search terms become encrypted and are excluded from the referrer headers that are sent to the sites you visit on the results page. The header data is not passed and the visited websites can see that a visitor came from Google, but they can no longer see which keyword term was used in the search query that produced that particular results page.
How does Google Encrypted impact search marketing?
Not all keyword data will be blocked from third party reporting tools. Search engine advertisers (Google Adwords accounts) in other words people who pay Google, will still have access to all of their individual keyword referral data. Google makes an exception to how they handle secured search for people who pay for the data via advertising. While the official explanation is that SSL search is all about “privacy” it is simply Google monetizing all of that data they capture from free Google analytics. The impact has been downplayed with Google indicating expected single digit percentages of “not provided”, but initial results tend to be much higher depending upon the industry vertical. Many websites see 12% to 18% of their keyword data as (not provided).
[fusion_builder_container hundred_percent=”yes” overflow=”visible”][fusion_builder_row][fusion_builder_column type=”1_1″ background_position=”left top” background_color=”” border_size=”” border_color=”” border_style=”solid” spacing=”yes” background_image=”” background_repeat=”no-repeat” padding=”” margin_top=”0px” margin_bottom=”0px” class=”” id=”” animation_type=”” animation_speed=”0.3″ animation_direction=”left” hide_on_mobile=”no” center_content=”no” min_height=”none”]
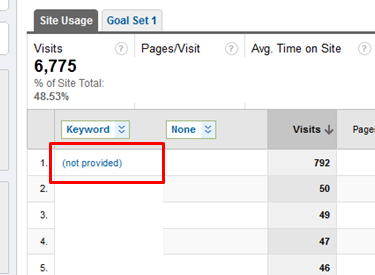
Keyword (not provided)
What does this mean for keyword focused search?
While striving to increase visibility for the “long tail”, it will not be wise to encourage organic keyword targeting as a performance metric. With an ever increasing volume of “not provided” terms it becomes even more challenging to prove or disprove what keyword phrases actually account for specific organic search traffic.
So just why are these changes important to understand?
With all of the feature changes to the SERP’s including Local results displayed, user behavior has changed and is continuing to transform. Click through rates are dropping on Page 1 results, as the query results evolve.
One recent study by Slingshot SEO shows compelling data suggesting only 52% of internet users on Google even click on page one results. This falls even further on Bing, only 26% of users click on a page one Bing results page. (from Slingshot SEO study on click through rates)
CTR study on 1st page behavior
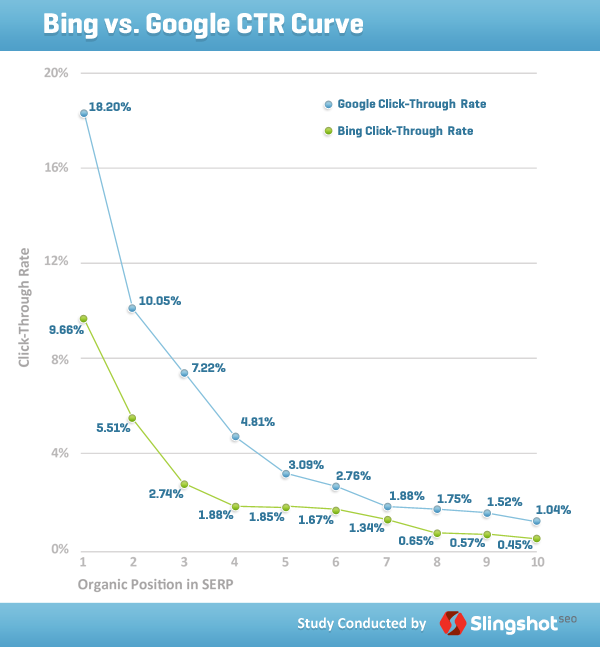
As more and more Rich Snippet data is pulled from websites and then displayed on the results page, it becomes increasing important to incorporate micro-data schema into the coding of web properties to maintain relevance in the search results.
The Bottom Line
The pace of search engine changes is increasing, so successful digital marketing strategies must be nimble and quick to response to market dynamics. However, with a strong base of optimization building a site from the ground up with basic search engine optimization blocking and tackling done correctly, strong online performance can be generated. Chasing after the “SEO tactics of the week” is a time waste. A great SEO strategy with proven optimization tactics will never go out of style and will always deliver rewarding results.
Connect with me – Circle Scott on Google+[/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]
A seasoned digital marketing professional with over 20 years of expertise in digital marketing, search engine optimization, search engine marketing, brand development, conversion optimization, lead generation, web development and data analytics. He is a strategic digital marketing thought leader in a multitude of business verticals including automotive, education, financial services, legal marketing and professional services.
 2. Duplicate content
2. Duplicate content




